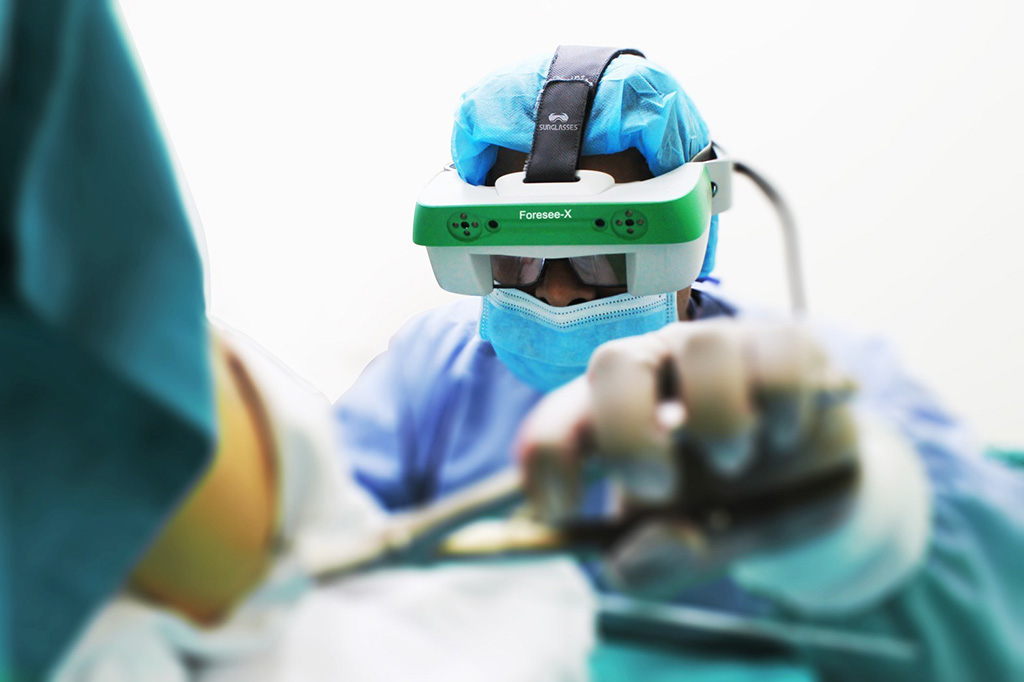
A set of smart surgical glasses with functionality based on augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) technologies brings a higher level of support to surgical trauma cases.
The Taiwan Main Orthopaedics Biotechnology Co. (Surglasses; Taichung, Taiwan) Foresee-X is a set of smart AR surgical glasses is designed to enhance intra-operative fluoroscopy image synchronization, primarily during orthopedic trauma procedures. Features include image enhancement functions, such as the ability to zoom in and out, allowing surgeons to concentrate on the operational field instead of monitors; reduced radiation exposure for the staff and patient; and improved accuracy by tracking the movements of surgical tools such as puncture needles, trocars, etc.
Image: The Foresee-X augment reality glasses (Photo courtesy of Surglasses)
The virtual and actual images are superimposed, and patient bone structure and tissues are fully visible through the smart glasses. In addition to improving overall surgical efficiency, the Foresee-X glasses can reduce OR staff radiation exposure by more than 60% compared to a mobile C-arm used for fluoroscopy. Foresee-X also allows outside observers to view procedures up close through tablet computers, as the device is equipped with an integrated camera with an 80 degree field of view that records video at 30 fps. The device can also collect data for academic purposes.
“The key to smart glasses is the algorithm. Since each person’s eyes have a different focal length, and with the addition of camera lens focus, synchronization would require the aid of high-performance computing,” said Min-Liang Wang, PhD, founder of Surglasses. “Furthermore, if the surgeon changes position during surgery, the image must be adjusted immediately for the new position. All of this can only be achieved by the development of cutting-edge technologies such as 5G and AR/MR.”
“Surglasses has been collaborating with hospitals in Taiwan and Malaysia to set up a specialized trauma center that includes Foresee-X as part of the equipment lineup. The smart surgical glasses are used for numerous kinds of orthopedic procedures including interlocking of nails, pelvic cases, wrists, shoulders, tibia, and many more,” said the company in a press statement. “With accuracy and efficiency as its main advantages, Foresee-X is the first of its kind on the market to provide cutting-edge assistance to surgeons and doctors dealing with trauma cases.”
AR is a term for a live direct or indirect view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are augmented by computer-generated sensory input. It is related to a general concept called mediated reality, in which a view of reality is modified–possibly even diminished rather than augmented–by a computer. As a result, the technology can enhance the perception of reality.